Exploring the realm of common social engineering techniques is crucial in today's digital landscape to protect against malicious cyber threats. From phishing attacks to impersonation schemes, understanding these tactics is key to enhancing cybersecurity measures.
This article delves into the intricate world of social engineering, shedding light on various strategies used by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals and organizations.
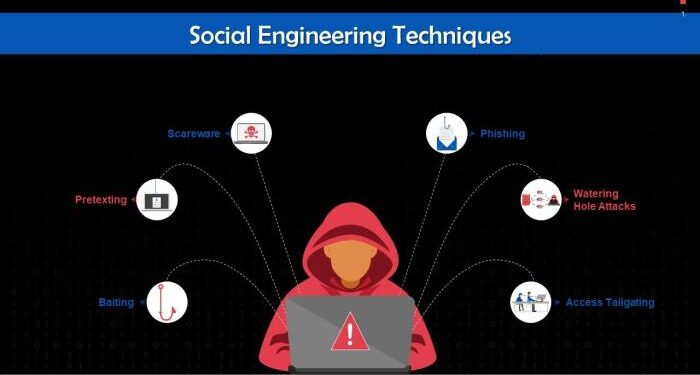
Introduction to Social Engineering Techniques
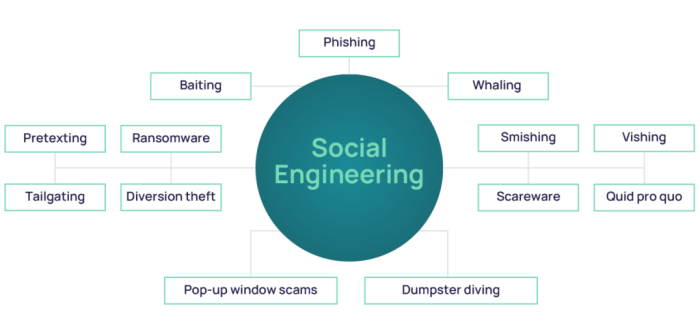
Social engineering in cybersecurity involves manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information or perform actions that compromise security. It relies on psychological manipulation rather than technical exploits.Understanding common social engineering techniques is crucial for safeguarding against cyber threats as it helps individuals and organizations recognize and prevent potential attacks.
By being aware of these tactics, people can better protect themselves from falling victim to social engineering schemes.
Real-World Scenarios
- Phishing Emails: Attackers send deceptive emails posing as legitimate entities to trick recipients into clicking on malicious links or sharing sensitive information.
- Pretexting: A scammer creates a fabricated scenario to gain the trust of a target and extract confidential details by pretending to be someone else, such as a trusted authority figure.
- Impersonation: Cybercriminals impersonate employees, customers, or other trusted individuals to manipulate victims into revealing sensitive data or performing unauthorized actions.
Phishing Attacks
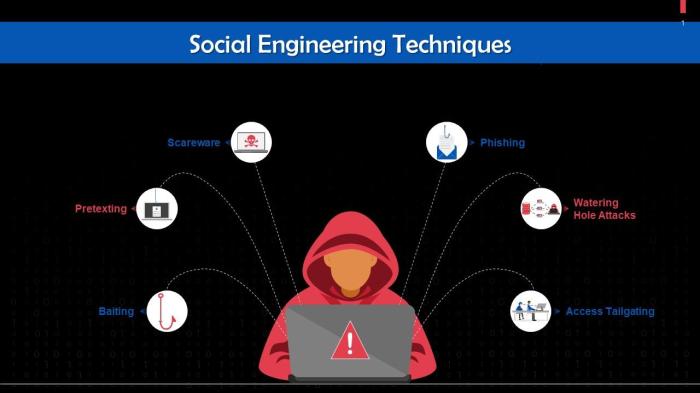
Phishing attacks are a type of social engineering attack where cybercriminals send fraudulent communications that appear to be from a reputable source in order to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as personal details, login credentials, or financial data.
These attacks are typically carried out through email, text messages, or phone calls, and often contain urgent requests or alarming messages to prompt the victim to act quickly without thinking.
Types of Phishing Attacks
- Spear Phishing: In this targeted form of phishing, attackers tailor their messages to a specific individual or organization, making them appear more legitimate and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Whaling: Similar to spear phishing, whaling targets high-profile individuals within an organization, such as executives or CEOs, to gain access to valuable information or funds.
- Pharming: This type of attack involves redirecting users to fake websites that mimic legitimate ones, tricking them into entering their credentials or financial information unknowingly.
Recognizing and Avoiding Phishing Attempts
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages: Do not click on links or download attachments from unknown senders.
- Verify the source: Check the sender's email address or phone number for any discrepancies or irregularities.
- Hover over links: Before clicking on a link, hover your mouse over it to see the actual URL and ensure it matches the expected destination.
- Use security software: Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-phishing software to help detect and block phishing attempts.
- Report suspicious activity: If you suspect a phishing attempt, report it to the relevant authorities or your organization's IT department.
Pretexting
Pretexting is a social engineering technique where an attacker creates a fabricated scenario to manipulate individuals into providing sensitive information or taking certain actions. This often involves building a false sense of trust or urgency to deceive the target.
Examples of Pretexting Techniques
- Creating a Fake Identity: An attacker may create a false persona, complete with fake credentials, to gain the trust of the target and extract information.
- Impersonating Someone Else: Pretending to be a trusted individual, such as a colleague or a service provider, to deceive the target into divulging sensitive data.
Protecting Against Pretexting Attacks
- Verify Requests: Always verify the identity of the person making a request for information, especially if it seems unusual or urgent.
- Be Cautious: Exercise caution when sharing personal or confidential information, even if the request appears legitimate.
- Educate Employees: Provide training to employees on recognizing and responding to pretexting attempts to enhance security awareness.
Baiting and Tailgating
Baiting and Tailgating are social engineering techniques used to gain unauthorized access by exploiting human behavior and trust. Baiting involves enticing an individual with a promise of something desirable in exchange for their credentials or access to sensitive information. For example, leaving infected USB drives in public spaces labeled as "Confidential" or "Salary Details" to tempt individuals into plugging them into their computers, unknowingly installing malware.Tailgating, on the other hand, involves an attacker following an authorized person into a restricted area by closely tailing them.
This can be seen in scenarios where someone holds the door open for a stranger without verifying their identity, allowing unauthorized access to a secure building.
Examples of Baiting and Tailgating Techniques
- An attacker leaves a USB drive labeled "Payroll Information" in a company parking lot, hoping an employee will pick it up and plug it into their work computer.
- A person follows an employee into a secure area by pretending to be on an urgent call and rushing in behind them without proper authentication.
Preventing Baiting and Tailgating Attacks
- Implement strict policies regarding the handling of unknown USB drives and other external storage devices.
- Encourage employees to question unfamiliar individuals attempting to gain access to restricted areas without proper authorization.
- Use access control mechanisms like key cards or biometric authentication to prevent unauthorized individuals from tailgating into secure locations.
Quid Pro Quo
Quid pro quo is a social engineering tactic where an attacker offers something in exchange for sensitive information or access. This can involve promising a reward or benefit in return for the victim's cooperation.Attackers use quid pro quo to manipulate victims by creating a sense of obligation or reciprocity.
By offering something of value, such as a gift, service, or opportunity, the attacker aims to establish trust and lower the victim's guard. Once the victim feels indebted or appreciative, they may be more likely to comply with requests for information or assistance.
How Attackers Use Quid Pro Quo
- Attackers may offer a free gift or service in exchange for login credentials or personal data.
- They may claim to be from a trusted organization or authority figure to gain credibility.
- By appearing helpful and friendly, attackers aim to build rapport and manipulate victims into sharing sensitive information.
Tips to Avoid Falling for Quid Pro Quo Schemes
- Avoid providing personal or sensitive information in exchange for freebies or rewards.
- Verify the identity of any individual or organization making requests for information or assistance.
- Be cautious of unsolicited offers or requests, especially if they seem too good to be true.
- Trust your instincts and be wary of anyone who tries to rush you into making a decision or sharing information.
Impersonation
Impersonation is a common social engineering technique where an attacker pretends to be someone else in order to gain access to sensitive information or manipulate the victim into taking certain actions.There are different forms of impersonation that cybercriminals may use to deceive individuals or organizations.
One example is CEO fraud, where the attacker poses as a company executive to trick employees into transferring funds or disclosing confidential data. Another form is tech support scams, where scammers impersonate technical support staff to gain remote access to a victim's computer or steal personal information.
Identifying Impersonation
- Be cautious of unsolicited communication: Verify the identity of the person contacting you, especially if they are requesting sensitive information or urgent action.
- Check for inconsistencies: Pay attention to details like email addresses, phone numbers, or language used that may not match the supposed identity of the individual.
- Use two-factor authentication: Implement additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access even if someone manages to impersonate a legitimate user.
- Report suspicious activity: If you suspect that you are being impersonated or targeted by a social engineering attack, report it to the appropriate authorities or your organization's IT department immediately.
Concluding Remarks
As we conclude our discussion on common social engineering techniques, it becomes evident that staying informed and vigilant is paramount in safeguarding against evolving cyber threats. By arming ourselves with knowledge and awareness, we can better protect our digital assets and personal information from falling into the wrong hands.
Top FAQs
How can individuals recognize phishing attempts?
Individuals can look out for suspicious email addresses, requests for personal information, and urgent calls to action in emails to identify potential phishing attempts.
What is the best way to protect against pretexting attacks?
Implementing strict verification procedures, training employees on recognizing social engineering tactics, and promoting a culture of security awareness can help protect against pretexting attacks.
How do baiting and tailgating attacks differ?
Baiting involves enticing individuals with promises of rewards, while tailgating involves unauthorized individuals following employees into secure areas without proper authorization.
What measures can organizations take to prevent impersonation attacks?
Organizations can establish clear communication channels, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct regular security awareness training to mitigate the risk of impersonation attacks.
Why is understanding quid pro quo tactics important for cybersecurity?
Understanding quid pro quo tactics helps individuals recognize manipulative schemes and avoid falling victim to deceptive offers in exchange for sensitive information.

![The 5 Best Laptops for Small Businesses in 2024 [All Budgets]](https://business.blogcristiano.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Top-5-Tech-Gadgets-for-Entrepreneurs-120x86.jpg)