Embark on a journey to explore the world of IoT devices and the crucial need to secure them effectively. From smart homes to industrial settings, the landscape of IoT devices is expanding rapidly, bringing both convenience and security risks. Let's delve into the realm of securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices to safeguard our privacy and data in this interconnected age.
As we navigate through the intricacies of IoT security, we uncover the essential steps and strategies that individuals and organizations can implement to protect their devices from cyber threats.
Understanding IoT Devices
IoT devices, or Internet of Things devices, are physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices differ from traditional devices by their ability to communicate and interact with each other without human intervention.
Common Types of IoT Devices
- Smart Home Devices: Examples include smart thermostats, smart lights, and smart security cameras that can be controlled remotely through a smartphone or voice commands.
- Wearable Devices: Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring devices fall under this category, collecting data on the user's activities and health metrics.
- Industrial IoT Devices: These devices are used in manufacturing plants, agriculture, and other industries to monitor and optimize processes, improve efficiency, and reduce downtime.
Benefits of IoT Devices
IoT devices offer numerous benefits in both everyday life and business operations. They can increase convenience, efficiency, and automation in homes and workplaces. For businesses, IoT devices can help in monitoring equipment, optimizing resources, improving decision-making through data analytics, and enhancing overall productivity.
Security Risks Associated with IoT Devices
IoT devices pose various cybersecurity threats due to their interconnected nature and potential vulnerabilities. These devices are susceptible to attacks that can compromise data privacy, network security, and even physical safety.
Cybersecurity Threats for IoT Devices
- 1. Botnet Attacks: Hackers can hijack IoT devices to create botnets for launching large-scale DDoS attacks, disrupting services.
- 2. Data Breaches: Weak security measures in IoT devices can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data stored or transmitted by these devices.
- 3. Malware Infections: IoT devices can be infected with malware, allowing attackers to control or manipulate them for malicious purposes.
- 4. Physical Tampering: Attackers can physically tamper with IoT devices to gain access to networks or compromise their functionality.
Real-World Incidents of IoT Compromises
- - In 2016, the Mirai botnet exploited vulnerable IoT devices to launch massive DDoS attacks, disrupting major websites and services.
- - A smart thermostat vulnerability in 2020 allowed hackers to access user data and control heating systems remotely.
- - Security cameras have been hacked to spy on individuals or homes, highlighting the risks of insecure IoT devices.
Consequences of Insecure IoT Devices
- - Privacy Breaches: Insecure IoT devices can lead to unauthorized access to personal data, compromising user privacy.
- - Safety Risks: Compromised IoT devices can pose physical safety risks, such as tampering with home security systems or medical devices.
- - Financial Losses: Attacks on IoT devices can result in financial losses for individuals and businesses, including ransom demands or data theft.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices
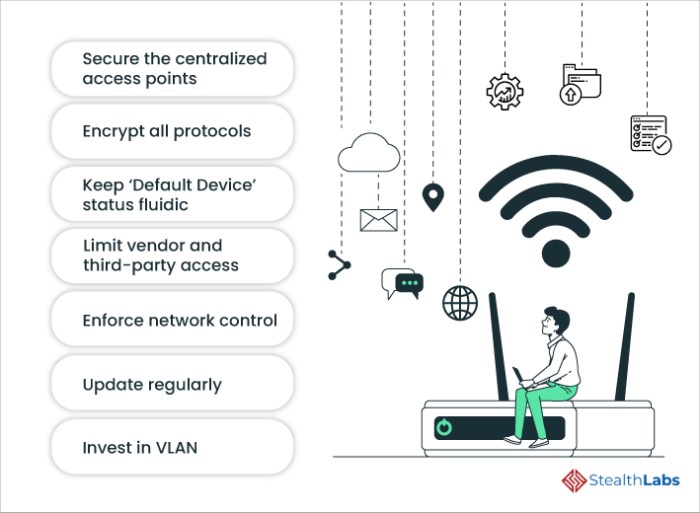
In order to enhance the security of IoT devices, individuals and organizations can implement the following best practices:
Regular Software Updates
- Regularly update the firmware and software of IoT devices to ensure they are equipped with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Set up automatic updates whenever possible to streamline the process and minimize the risk of missing critical updates.
- By keeping devices up to date, users can mitigate vulnerabilities and protect against potential security breaches.
Strong Passwords
- Create unique, complex passwords for each IoT device to prevent unauthorized access.
- Avoid using default passwords that are easy to guess, and opt for a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Regularly change passwords and avoid reusing them across multiple devices to enhance security measures.
Encryption for Data Protection
- Implement encryption protocols to secure data transmitted between IoT devices and networks.
- Utilize strong encryption algorithms to safeguard sensitive information from potential cyber threats.
- Encryption plays a crucial role in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged by IoT devices.
Network Security for IoT Devices
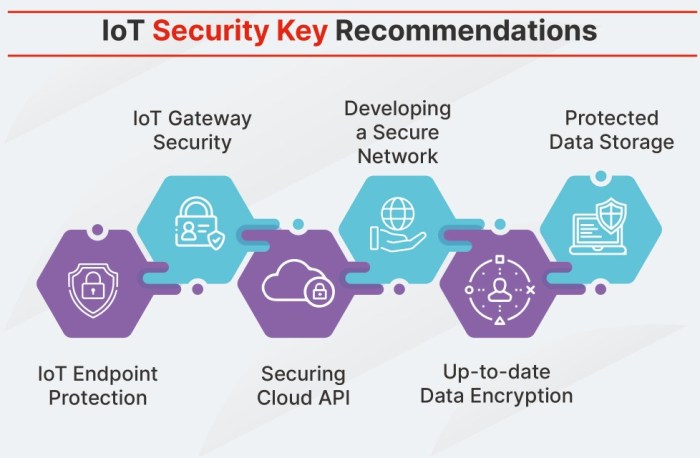
Network security is crucial for protecting IoT devices from cyber threats. One effective way to enhance the security of IoT devices is through network segmentation. By dividing the network into separate segments, each with its own security controls and access policies, organizations can isolate IoT devices from other parts of the network, reducing the impact of a potential breach.
Use of Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
- Firewalls play a key role in securing IoT networks by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. They act as a barrier between IoT devices and the internet, filtering out malicious traffic and unauthorized access attempts.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are designed to detect and respond to suspicious activities or security breaches within the network. By analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying anomalies, IDS can help in identifying potential threats to IoT devices.
Zero-Trust Security for IoT Device Protection
- Zero-trust security is a security model that assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, regardless of their location within the network. This approach requires verification of every user and device attempting to access the network, reducing the attack surface and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to IoT devices.
- Implementing zero-trust security for IoT devices involves strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users and devices can interact with IoT devices.
Final Summary

In conclusion, securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices is not just a matter of convenience but a necessity in today's digital era. By adopting best practices and staying vigilant against potential risks, we can ensure a safer and more secure connected environment for all.
FAQ Overview
What are some common types of IoT devices?
Common types include smart thermostats, security cameras, wearable fitness trackers, and connected appliances.
How can individuals secure their IoT devices?
Individuals can secure their devices by regularly updating software, using strong passwords, and enabling two-factor authentication where possible.
What is the role of encryption in IoT security?
Encryption plays a crucial role in protecting data transmitted by IoT devices, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure and private.


![The 5 Best Laptops for Small Businesses in 2024 [All Budgets]](https://business.blogcristiano.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Top-5-Tech-Gadgets-for-Entrepreneurs-120x86.jpg)